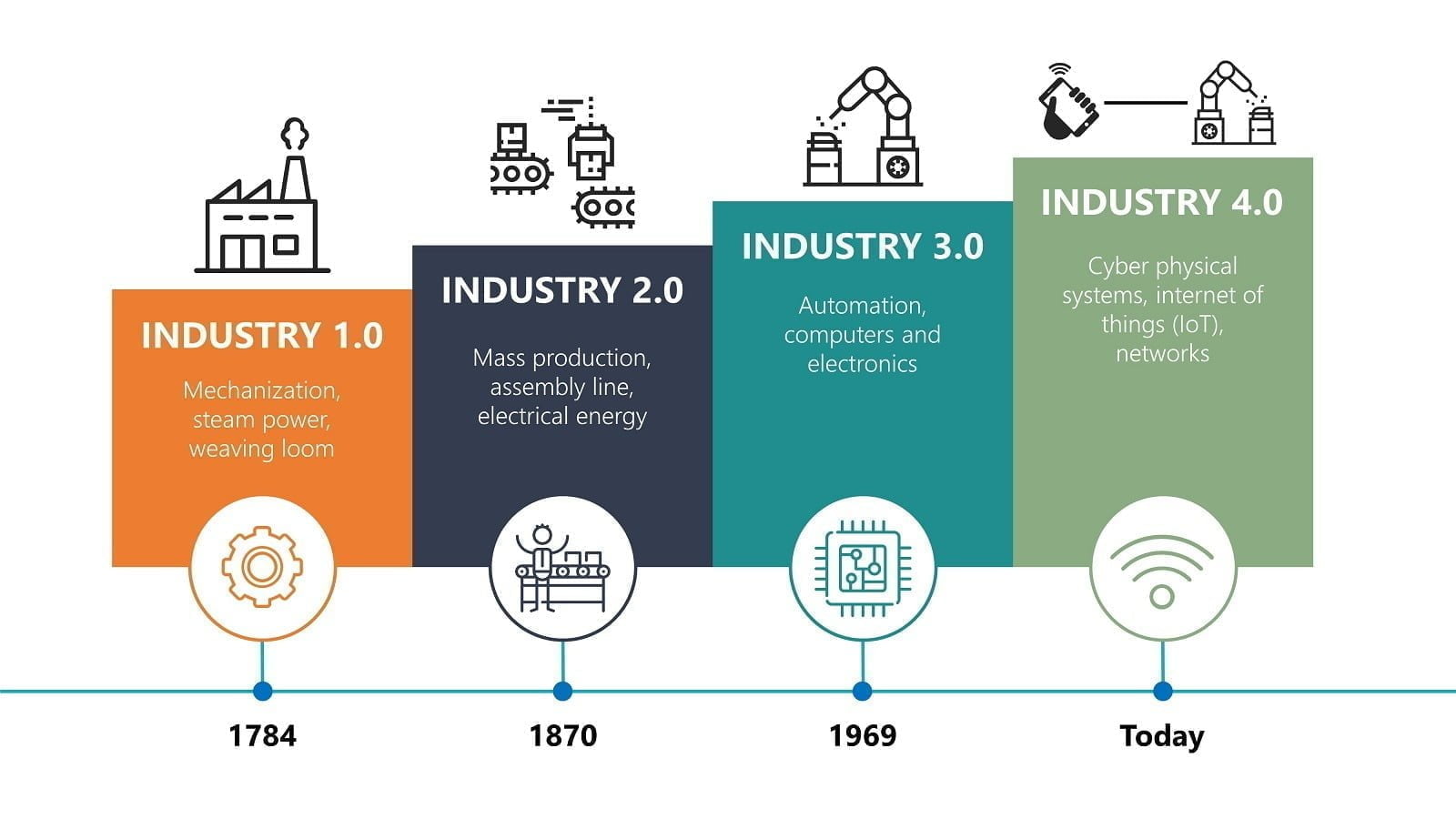
- Ease of communication and operation. This relates to the possibility for signals and data to be communicated between machines and people using the internet. It also addresses the possibility for remote control and action in case of an emergency. Can machines initiate processes on their own? Is it possible for humans to interfere with these processes when necessary?
- Accessibility of information. Feeding sensor data to digital plant models makes it possible for information systems to replicate virtual versions of physical realities. This is impossible without the assemblage of sensor data to a form that can be interpreted by other digital devices. Majorly, you are finally able to decipher the information and use it for diverse purposes.
- Technical Support. This deals with the ability of machines to collect information and interpret it for decision making. Hence, a machine will be able to tackle emergent situations almost instantly. Additionally, processes and tasks that may endanger human life can be carried out by cyber physical systems. Humans may not be able to provide the needed power to perform certain tasks and even if they do, the unpleasant nature of those tasks may repulse humans but not machines.
- Except for cases where there are conflicting goals, decision making in Industry 4.0 is decentralized so that these cyber physical systems can make their own decisions based on the signals and data they receive.
- Chief among them is the issue of IT security. Now that robots will control machinery remotely, it becomes prone to hacking and the issue of security will have to be taken seriously. Proprietary production knowledge, once transmitted via the internet for action by a robot becomes vulnerable too.
- The communication between machines also need to be reliable and stable. When information is passed via the internet, loss time needs to be almost zero because machines are about precision. If there is a lag of even about a microsecond, it can spell doom for the entire smart factory.
- There is the tendency that many high paying jobs will be lost because their roles will become redundant. On the flip side, the technical prowess needed to fully implement industry 4.0 is still in short supply. So, start learning to get ahead.
- Generally, stakeholders are usually averse to change and if the decision makers do not make a commitment to explore Industry 4.0, we may have to wait a little longer. Its inevitability is however written on the wall already.
Undoubtedly, big data analytics is a major player in Industry 4.0. DataPoint industrial edition will ensure that at least four of the 6Cs that give Industry 4.0 a momentous fighting chance are provided. These are:
- Connection
- Content and Context
- Community and
- Customization
Owing to the fact that DataPoint Industrial edition can read data from Object Linking and Embedding for Process Control (OPC), it can serve as the liaison between robots and the information screen. Basically, it is digital signage for the industry. You can display data from OPC in real time on your screen.